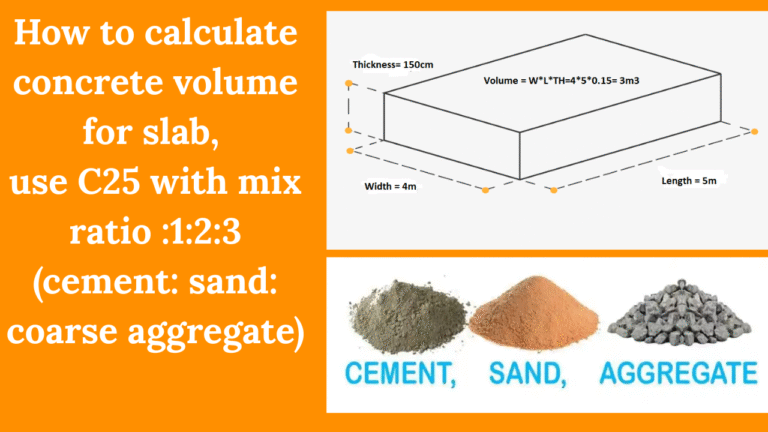
The Functions, Duties, and Significance of Quantity Surveying in the Construction Sector
Introduction to Quantity Surveying
Construction is one of the most resource-intensive industries in the world, requiring precise planning, effective management, and accurate financial forecasting to deliver projects successfully. Among the professionals who make this possible, Quantity Surveyors (QS) stand out as the financial and contractual managers of construction projects. To put it simply, a quantity surveyor makes sure that building projects are finished on schedule, within budget, and to the necessary quality standards. Without them, construction projects risk spiraling into financial chaos, legal disputes, and mismanagement of resources.
Definition and Meaning of Quantity Surveying
Quantity Surveying can be defined as the science and practice of controlling costs in construction projects, from initial design to final completion. The discipline encompasses budgeting, cost estimation, contract management, tendering, and financial reporting. Essentially, a Quantity Surveyor acts as the “financial watchdog” of construction projects, ensuring resources are utilized efficiently.
Historical Background and Evolution of Quantity Surveying
The roots of Quantity Surveying date back to the 17th century in England, where surveyors were initially tasked with measuring and estimating construction works. Over time, as construction projects became larger and more complex, the role evolved into a specialized profession that focused on cost management and contract administration. Today, Quantity Surveying is recognized globally as an essential profession in the construction industry, with professional bodies such as RICS (Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors) setting international standards.
Why Quantity Surveying Matters in Modern Construction
In the current construction business, which is extremely competitive and cost-sensitive, quantity surveying is essential. With materials, labor, and technology costs fluctuating constantly, projects require a professional who can balance financial feasibility with design aspirations. A QS ensures transparency in procurement, minimizes financial risks, and contributes to delivering value for money. Without their expertise, projects could face significant cost overruns and disputes, leading to failure.
The Role of a Quantity Surveyor in Construction
The role of a Quantity Surveyor goes far beyond simply calculating numbers. They are involved in every stage of a project—before construction begins, while it is ongoing, and even after completion.
Overview of Quantity Surveyor’s Duties
At its core, a QS ensures that every penny spent on a project is justified. This involves preparing cost estimates, managing contracts, negotiating with contractors, and monitoring expenses throughout the project lifecycle. They act as the bridge between clients, contractors, architects, and engineers, ensuring financial and contractual clarity.
Pre-Construction Roles and Responsibilities
Before construction begins, a Quantity Surveyor is heavily involved in project feasibility studies and cost planning. They assess whether the project is financially viable and prepare detailed budgets. They also assist clients in choosing procurement methods, drafting tender documents, and evaluating contractor bids. This phase is crucial, as accurate cost estimation ensures the client can secure the necessary funding and avoid financial shocks later.
During Construction: Monitoring and Managing Costs
Once the project kicks off, the QS becomes the cost controller. They monitor construction expenditures against the budget, prepare interim payment certificates for contractors, and track any variations in design or scope that may impact costs. Their role ensures that the project stays financially sustainable, and any issues are flagged early to avoid unexpected overruns.
Post-Construction Responsibilities
After the completion of construction, the Quantity Surveyor finalizes project accounts, ensures contractors are paid correctly, and evaluates whether the project was delivered within the financial framework agreed upon. They may also assist in resolving disputes related to costs and claims. This final phase highlights the QS’s role as a guardian of financial accountability, ensuring clients receive maximum value for their investment.
Key Responsibilities of a Quantity Surveyor
Quantity Surveyors juggle a wide range of responsibilities that ensure construction projects are both financially and contractually sound.
Cost Estimation and Budgeting
One of the most vital responsibilities of a QS is to estimate project costs accurately. They calculate expenses related to materials, labor, machinery, and professional services. By forecasting potential risks and accounting for inflation, QS professionals prepare reliable budgets that guide decision-making.
Tendering and Procurement
Quantity Surveyors oversee the tendering process, where contractors submit bids for construction projects. They prepare tender documents, evaluate bids, and recommend the most suitable contractor. This ensures transparency and fairness while securing the best value for the client.
Contract Management
Managing contracts is another critical responsibility. The QS ensures that terms and conditions are adhered to, manages variations, and handles claims from contractors. Effective contract management minimizes disputes and provides legal clarity.
Risk Management and Value Engineering
Every construction project faces risks—be it financial, legal, or operational. A QS identifies potential risks early and develops strategies to mitigate them. They also employ value engineering techniques, finding ways to achieve the same quality at lower costs without compromising performance.
Dispute Resolution and Negotiation
Conflicts are common in construction projects, often arising from payment issues, delays, or variations. Quantity surveyors serve as mediators, resolving conflicts amicably by applying their understanding of contracts and expenses. Their negotiation skills are crucial in maintaining good relationships among stakeholders.
Importance of Quantity Surveying in the Construction Industry
In the construction industry, disputes, delays, and cost overruns are frequent occurrences. This is where Quantity Surveying proves its value.
Ensuring Cost Efficiency
With tight budgets and fluctuating material prices, controlling costs is paramount. A QS ensures that every expenditure aligns with the project budget, preventing financial wastage.
Enhancing Project Quality and Standards
Cost control does not mean cutting corners. A QS balances financial efficiency with quality by ensuring materials and processes meet industry standards. This enhances the durability and performance of the finished structure.
Supporting Legal and Contractual Compliance
Contracts are legally enforceable agreements that specify the responsibilities of a project. A QS ensures compliance with these contracts, protecting clients from potential lawsuits and financial penalties.
Contribution to Sustainable Construction
Sustainability is now a global construction priority. QS professionals play a vital role in promoting eco-friendly practices by recommending cost-effective, sustainable materials and monitoring resource use efficiently.
Skills and Competencies of an Effective Quantity Surveyor
The effectiveness of a Quantity Surveyor is not just about technical expertise; it lies in a combination of diverse skills that allow them to manage costs, contracts, and relationships seamlessly. A well-rounded QS is a hybrid professional—part economist, part lawyer, part engineer, and part negotiator. Let’s dive deeper into the skills that make them indispensable.
Technical Skills
At the core, a Quantity Surveyor must possess strong technical knowledge in construction methods, materials, and project management. They must understand engineering drawings, specifications, and building codes to accurately estimate costs and identify potential risks. Familiarity with tools like CAD, cost management software, and BIM (Building Information Modelling) is becoming increasingly important. A QS who is tech-savvy can analyze data faster, reduce errors, and provide accurate cost forecasts, which are essential for large-scale projects.
Financial and Analytical Skills
Budgeting and financial analysis are the backbone of Quantity Surveying. A QS must be adept at preparing detailed cost estimates, analyzing financial reports, and forecasting cash flow. They often handle millions of dollars in budgets, meaning one small error can lead to significant financial consequences. Analytical skills enable them to evaluate various scenarios, predict potential risks, and recommend cost-saving alternatives without compromising quality.
Communication and Negotiation Skills
Quantity Surveyors often find themselves at the negotiation table with contractors, suppliers, and clients. Clear understanding of project needs, financial ramifications, and contractual duties is ensured via effective communication. Strong negotiation skills help in securing favorable contracts, resolving disputes, and maintaining relationships that foster long-term collaborations.
Leadership and Team Collaboration Skills
Construction projects are complex and involve multiple stakeholders. A QS must lead financial discussions, coordinate with architects and engineers, and ensure smooth collaboration. Their ability to manage people, resolve conflicts, and align diverse teams toward the same goal makes them more than just number crunchers—they become project leaders.
Challenges Faced by Quantity Surveyors
Although becoming a quantity surveyor has many benefits, there are drawbacks as well. Resilience, flexibility, and problem-solving abilities are necessary to overcome these challenges.
Dealing with Project Delays and Budget Overruns
Delays in construction are common due to weather conditions, supply chain issues, or labor shortages. Each delay translates into financial implications, and it’s the QS’s job to manage these extra costs. Keeping budgets under control during such disruptions is one of the toughest challenges.
Managing Stakeholder Expectations
Clients often want projects completed quickly and at minimal cost, while contractors seek higher profits Clear communication and diplomacy are necessary to balance these expectations. A QS must maintain transparency, providing realistic forecasts to avoid disappointment.
Legal and Contractual Disputes
Construction contracts are complex and disputes can arise over payments, delays, or scope changes. A QS frequently steps in as a mediator, using their expertise to interpret contracts fairly. This can be challenging, especially when both sides hold strong, conflicting positions.
Keeping Up with Technological Advancements
With rapid digital transformation, QS professionals must continuously adapt to new software, BIM technologies, and artificial intelligence tools. While these tools improve efficiency, they also demand constant learning and adaptation. A QS who fails to evolve risks becoming obsolete in a competitive market.
The Future of Quantity Surveying
The function of quantity surveyors is changing quickly along with the building sector. The future promises exciting opportunities, but only for those ready to embrace change.
Digital Transformation in Construction
Digital tools like Building Information Modelling (BIM), drones, and advanced cost management software are revolutionizing construction. Quantity Surveyors will increasingly rely on real-time data to monitor progress, track costs, and predict potential financial risks. Those who embrace digitalization will remain competitive, while others may struggle to keep pace.
Quantity Surveyors as Sustainability Champions
Sustainability is no longer optional—it’s a necessity. QS professionals will increasingly focus on green construction practices, ensuring materials and processes are environmentally friendly and cost-effective. They will play a pivotal role in guiding clients toward eco-friendly alternatives without blowing the budget.
Global Demand and Career Opportunities
Quantity Surveying is not limited to one region—it’s a global profession. As construction booms in emerging markets like Asia and Africa, the demand for skilled QS professionals is rising. With international certifications like RICS, a Quantity Surveyor can work anywhere in the world, making it a truly global career.
Case Studies of Successful Quantity Surveying in Projects
The best way to understand the value of Quantity Surveyors is to look at real-world examples where their expertise turned potential failures into success stories.
Large-Scale Infrastructure Projects
Think of large-scale projects like bridges, airports, and highways. In these cases, cost overruns can reach billions if not carefully managed. Quantity Surveyors play a central role in financial planning, ensuring governments and investors get value for money. For example, major international airports often rely heavily on QS professionals to balance budgets against complex engineering demands.
Residential and Commercial Building Projects
In housing developments or commercial towers, QS professionals ensure developers achieve profitability while maintaining quality. They negotiate with contractors, recommend cost-effective materials, and ensure projects meet timelines. Their presence often means the difference between a profitable venture and a financial disaster.
International Examples of Quantity Surveying Excellence
Globally, there are numerous examples of Quantity Surveyors preventing major disputes through their contractual and financial expertise. From Dubai’s skyscrapers to London’s Olympic venues, QS professionals have played crucial roles in ensuring that world-class projects were delivered within budget and on time.
Conclusion
Quantity Surveying is not just about numbers—it is about ensuring financial discipline, contractual fairness, and sustainable progress in the construction industry. Quantity Surveyors act as the financial guardians of projects, ensuring that clients get value for money, contractors are fairly compensated, and resources are used responsibly.
Looking ahead, the role of a QS will continue to grow in importance. With digital tools, and sustainability becoming central to construction, Quantity Surveyors will evolve into even more influential professionals shaping the future of the built environment. For anyone aspiring to join the profession, the future is bright, global, and impactful.